Germany passed bill to make energy saving compulsory for all sectors
- September 22, 2023
- Posted by: Quatro Strategies
- Categories: ESG & Renewable Energy, Europe, Sanctions & Regulation

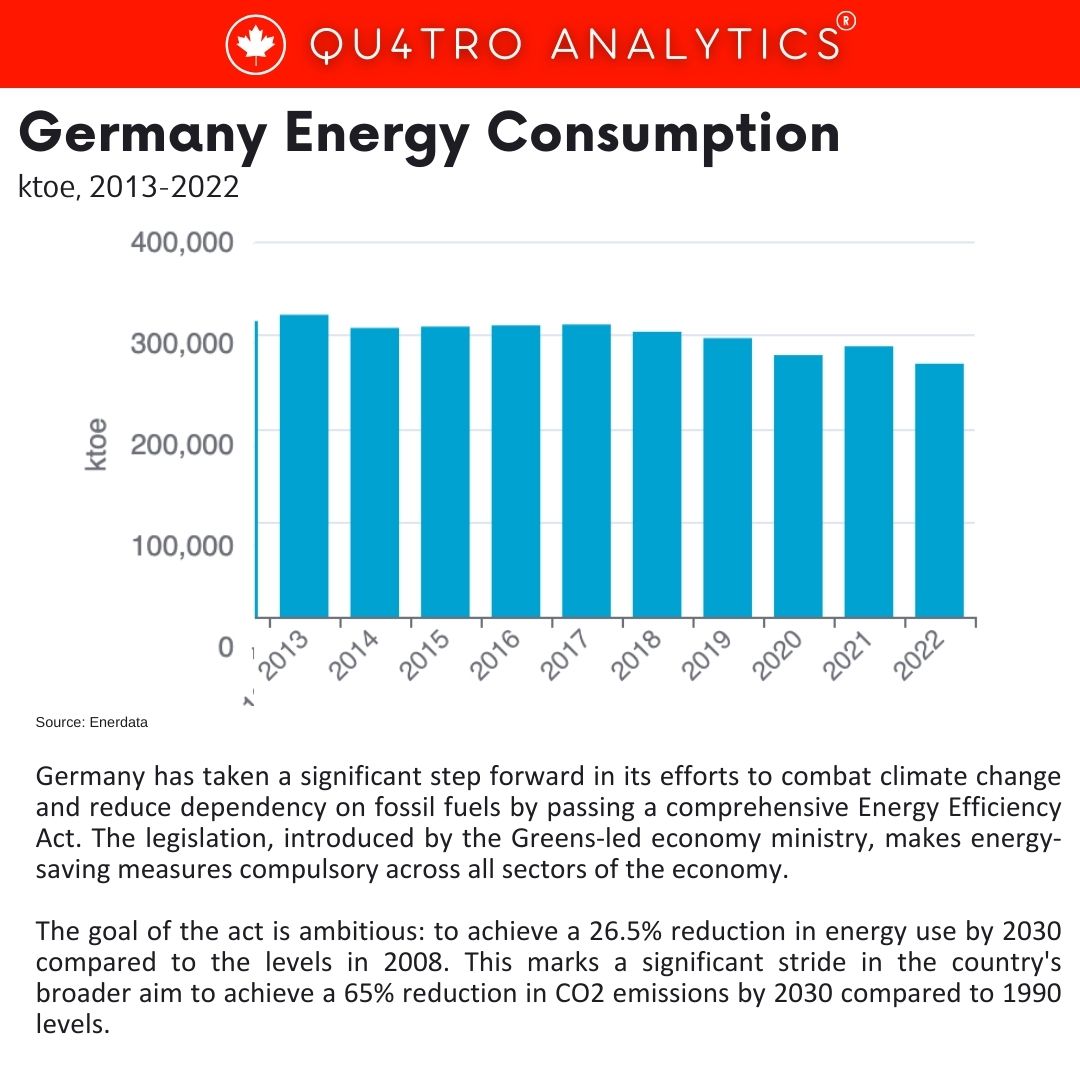
Germany has taken a significant step forward in its efforts to combat climate change and reduce dependency on fossil fuels by passing a comprehensive Energy Efficiency Act. The legislation, introduced by the Greens-led economy ministry, makes energy-saving measures compulsory across all sectors of the economy. The goal of the act is ambitious: to achieve a 26.5% reduction in energy use by 2030 compared to the levels in 2008. This marks a significant stride in the country’s broader aim to achieve a 65% reduction in CO2 emissions by 2030 compared to 1990 levels.
The act encompasses various regulations for energy savings, targeting public buildings, industries, and the rapidly growing data center sector across Germany. However, while the legislation mandates companies to formulate energy-saving plans, it does not impose binding measures, according to a spokesperson for the German Energy Efficiency Initiative, a network of companies advocating for robust energy efficiency policies.
Some critics express doubts about whether the law, as it stands, would align with EU regulations or prove adequate for Germany to meet its ambitious 2030 climate goals.
 Germany has been spurred into action by concerns about the persistent low supply of Russian gas, which could potentially lead to energy shortages. The government had introduced some initial energy-saving measures in the previous year, such as banning heating for private swimming pools and promoting work-from-home arrangements.
Germany has been spurred into action by concerns about the persistent low supply of Russian gas, which could potentially lead to energy shortages. The government had introduced some initial energy-saving measures in the previous year, such as banning heating for private swimming pools and promoting work-from-home arrangements.
Despite this, the country missed its 2020 target of a 20% reduction in energy consumption from 2008 levels. Notably, in 2022, Germany achieved its lowest energy consumption since 1990, according to data from the Federal Environment Agency.
The European Union has set targets to reduce final energy consumption across its member states by 11.7% by 2030, compared to energy consumption forecasts made in 2020. However, industrial lobbies’ pressure has led to a diluted version of the law from its original draft, removing targets for industrial companies and consumption beyond 2030.
The new law has faced criticism, with industrial representatives arguing that it lacks positive incentives for energy savings and may pose legal uncertainty while limiting growth. Despite this, Berlin remains optimistic that incentives to encourage more efficient and eco-friendly heaters, along with expected rising carbon pricing, will contribute to improving energy efficiencies in the country.
By QUATRO Strategies International Inc.
QUATRO Strategies International Inc. is the leading business insights and corporate strategy company based in Toronto, Ontario. Through our unique services, we counsel our clients on their key strategic issues, leveraging our deep industry expertise and using analytical rigor to help them make informed decisions to establish a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Interested in learning more?
Sign up for Top Insights Today

Top Insights Today delivers the latest insights straight to your inbox.
You will get daily industry insights on
Oil & Gas, Rare Earths & Commodities, Mining & Metals, EVs & Battery Technology, ESG & Renewable Energy, AI & Semiconductors, Aerospace & Defense, Sanctions & Regulation, Business & Politics.


