China’s export restriction on gallium push prices higher
- August 19, 2023
- Posted by: Quatro Strategies
- Categories: AI & Semiconductors, China
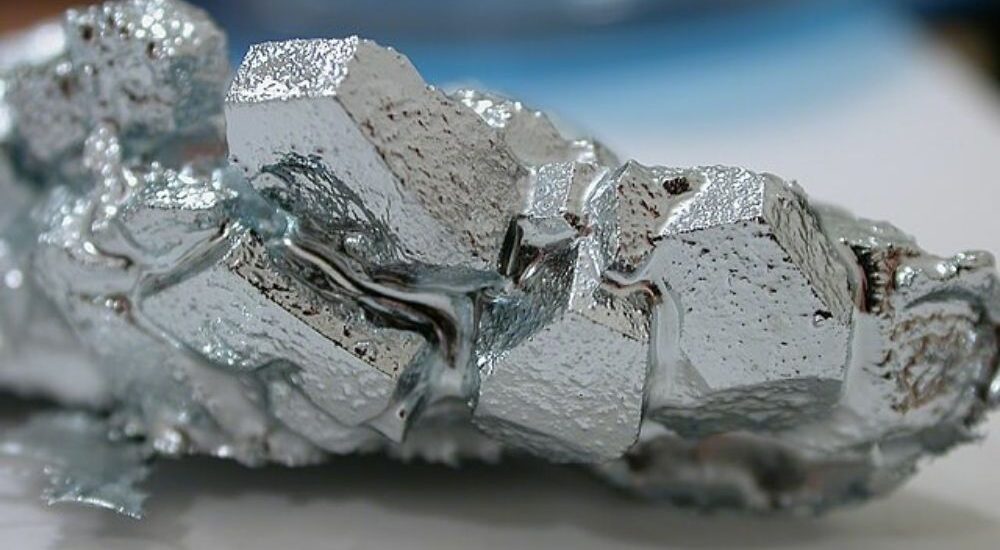

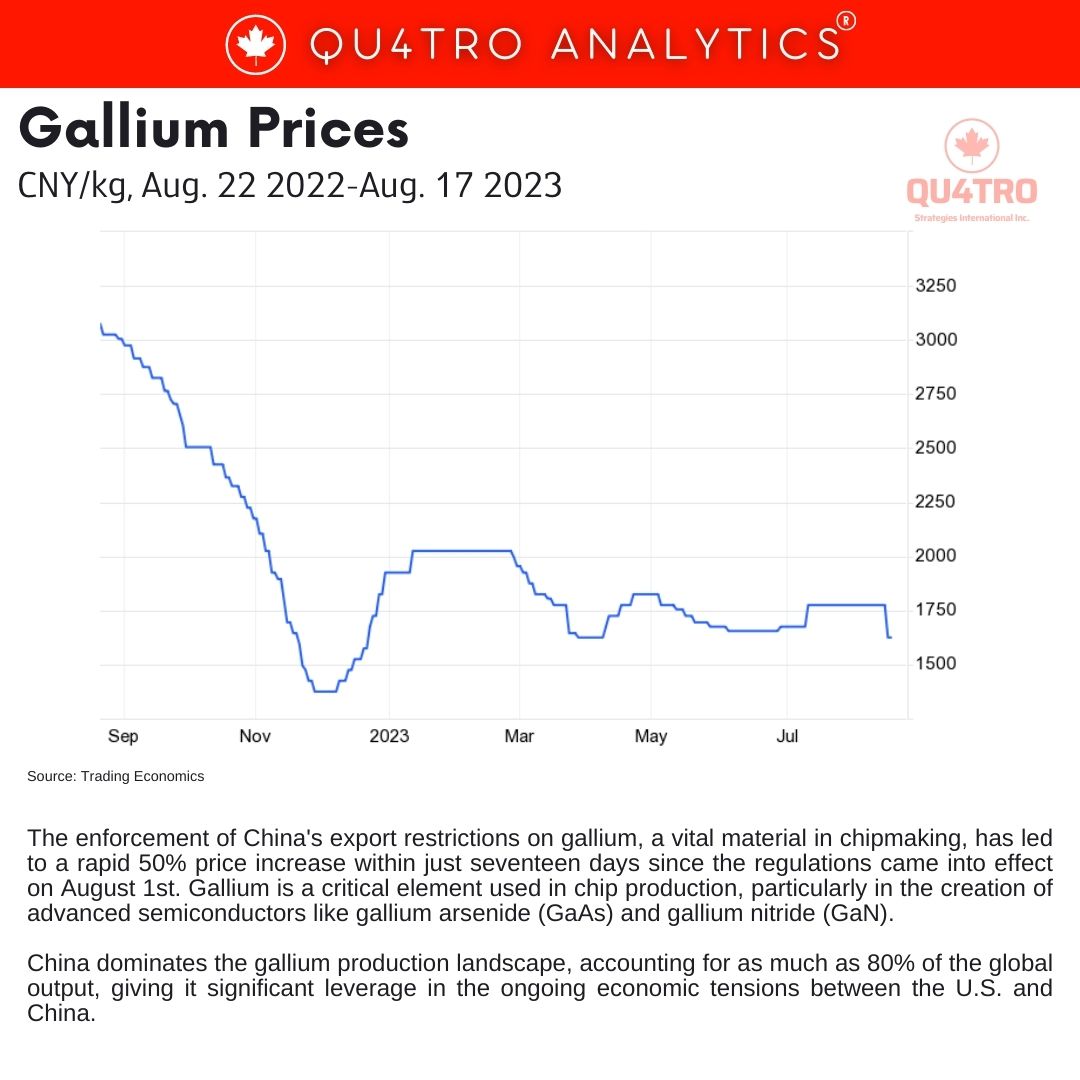
The enforcement of China’s export restrictions on gallium, a vital material in chipmaking, has led to a rapid 50% price increase within just seventeen days since the regulations came into effect on August 1st. Gallium is a critical element used in chip production, particularly in the creation of advanced semiconductors like gallium arsenide (GaAs) and gallium nitride (GaN). China dominates the gallium production landscape, accounting for as much as 80% of the global output, giving it significant leverage in the ongoing economic tensions between the U.S. and China.
This price surge has driven gallium prices to a 10-month high of $400 per kilogram, posing challenges for chipmakers and companies that rely on this material, even in trace amounts, for high-performance semiconductor designs. To put this in perspective, high-purity silicon metal (Si) costs an average of $2,000 per metric ton, making a kilogram of silicon worth just $2.
Most gallium refinement facilities are concentrated in China and Japan, with a lone facility located in Europe. However, the limited presence of production facilities outside China and the quick implementation of the export restrictions have created supply challenges for the global market, leaving non-producing countries heavily reliant on importing the base metal or processed gallium arsenide wafers.
 The export restrictions imposed by China require U.S.-based entities to register with China’s Ministry of Commerce to import gallium. However, companies were only allowed to apply for licenses starting on August 1st, the same day the restrictions took effect. Obtaining a license can take up to 45 days, creating significant disruptions for companies seeking to secure gallium supply.
The export restrictions imposed by China require U.S.-based entities to register with China’s Ministry of Commerce to import gallium. However, companies were only allowed to apply for licenses starting on August 1st, the same day the restrictions took effect. Obtaining a license can take up to 45 days, creating significant disruptions for companies seeking to secure gallium supply.
While China is a major producer of gallium, its chipmaking capabilities lag behind the U.S., with a five-generation gap in advanced microelectronics. This means that China may not immediately benefit from the restrictions in terms of chip production but can use them strategically to stockpile gallium for future deployment once its chip manufacturing processes catch up.
The sudden surge in gallium prices and the tightening of supply highlight the vulnerability of global supply chains, especially when a single country has significant control over critical materials. This situation underscores the ongoing challenges in balancing geopolitical tensions, technological competition, and the intricacies of global trade in the semiconductor industry.
Interested in learning more?
Sign up for Top Insights Today

Top Insights Today delivers the latest insights straight to your inbox.
You will get daily industry insights on
Oil & Gas, Rare Earths & Commodities, Mining & Metals, EVs & Battery Technology, ESG & Renewable Energy, AI & Semiconductors, Aerospace & Defense, Sanctions & Regulation, Business & Politics.


