Japan, Namibia sign rare earths exploration deal
- August 21, 2023
- Posted by: Quatro Strategies
- Categories: Africa, Asia Pacific, Mining & Metals, Rare Earths & Commodities

Japan has taken a significant step in its pursuit of diversifying its supply chain for critical minerals by signing an agreement with Namibia to jointly explore for rare earth minerals. This move is part of Japan’s broader strategy to reduce its reliance on China, which currently dominates the global supply of these essential minerals used in various industries, including electric vehicle (EV) batteries.
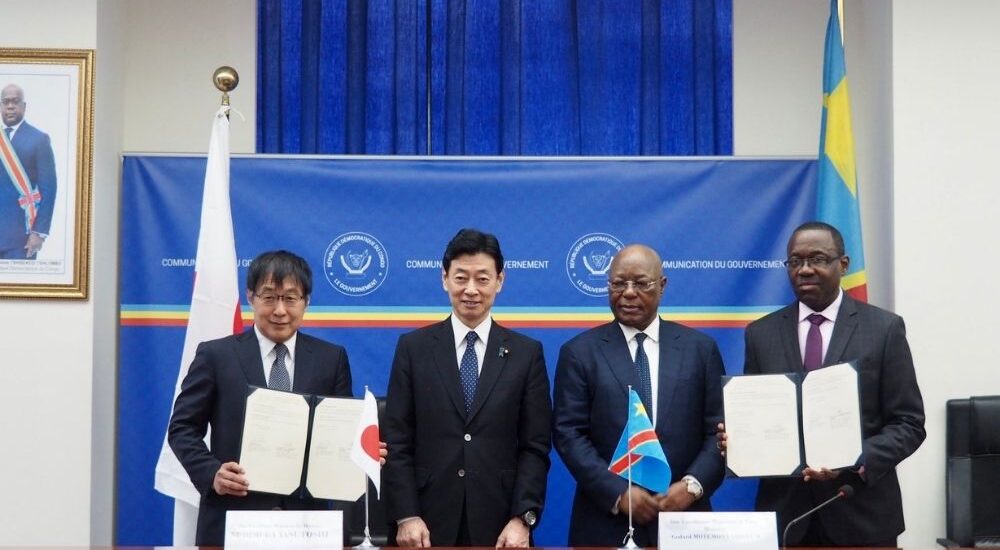
The agreement was signed between the Japan Organization for Metals and Energy Security (JOGMEC) and Namibia’s state-owned mining firm, Epangelo. While the details of the agreement have not been immediately disclosed, it marks a significant step forward in Japan’s efforts to secure a stable supply of rare earth minerals that are crucial for the manufacturing of EV batteries and other advanced technologies.
Yasutoshi Nishimura, Japan’s Minister for Economy, Trade and Industry, has been actively engaged in this initiative, visiting countries with substantial deposits of rare earths, including Namibia, Zambia, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. The goal is to establish a supply chain of critical minerals in Africa, allowing Japan to reduce its dependence on China for these essential resources.
One of the primary motivations behind Japan’s efforts to diversify its supply chain is to ensure the stability of resources needed for its growing electric vehicle industry. Rare earth minerals are integral to the production of EV batteries, as they are used in the creation of powerful and efficient magnets that play a crucial role in battery performance.
JOGMEC is already involved in a partnership with Namibia Critical Metals Inc. for the development of the Lofdal deposit in northwestern Namibia. This deposit is rich in yttrium and has the potential for substantial production of dysprosium and terbium, two valuable heavy rare earth elements. These elements are essential for creating the permanent magnets used in electric cars and renewable energy technologies like wind turbines.
Namibia itself has been proactive in securing partnerships for rare earth mineral supply. In 2022, the country signed an agreement to supply rare earth minerals to the European Union, further solidifying its position as an important player in the global supply chain for these critical resources.
Japan’s agreement with Namibia represents a significant stride toward establishing a more secure and diversified supply chain for rare earth minerals. As the world’s demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies continues to rise, such initiatives become increasingly vital for the stability and sustainability of global industries.
Interested in learning more?
Sign up for Top Insights Today

Top Insights Today delivers the latest insights straight to your inbox.
You will get daily industry insights on
Oil & Gas, Rare Earths & Commodities, Mining & Metals, EVs & Battery Technology, ESG & Renewable Energy, AI & Semiconductors, Aerospace & Defense, Sanctions & Regulation, Business & Politics.