China’s manufacturing woes hit copper imports
- August 20, 2023
- Posted by: Quatro Strategies
- Categories: China, Rare Earths & Commodities

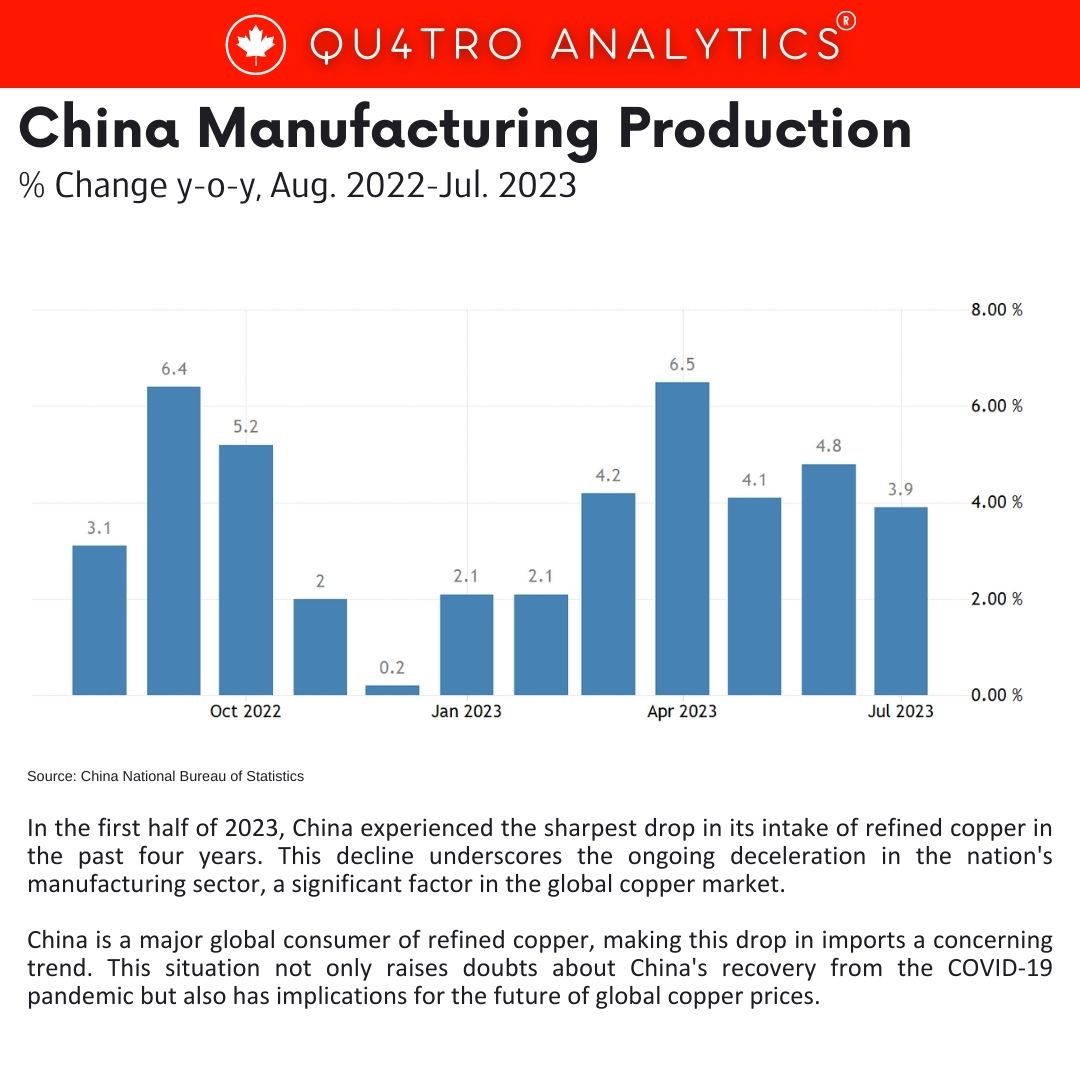
In the first half of 2023, China experienced the sharpest drop in its intake of refined copper in the past four years. This decline underscores the ongoing deceleration in the nation’s manufacturing sector, a significant factor in the global copper market. China is a major global consumer of refined copper, making this drop in imports a concerning trend. This situation not only raises doubts about China’s recovery from the COVID-19 pandemic but also has implications for the future of global copper prices.
The decrease in copper imports persisted through July, with customs data revealing a 2.7% decline in copper imports compared to the previous year. In July, China imported 451,159 metric tons of unwrought copper and copper products, indicating a weakening demand within the economy. China’s manufacturing activity has contracted for the fourth consecutive month in July, and its industrial profits have continued to decline for the sixth month of this year, putting additional pressure on copper demand.
Analysts attribute this reduction in copper imports to both lackluster demand within the struggling economy and elevated global copper prices. They suggest that a governmental stimulus might be necessary to revive the market. Such stimulus could help invigorate internal demand and counterbalance the subdued export markets. However, it’s important to note that while imports of refined copper are declining, imports of copper raw materials into China remain robust, contributing to a surge in domestic refined metal production.
 Although China’s imports of refined copper have been decreasing, imports of copper raw materials, particularly from Russia, have been moving in the opposite direction. Import patterns for refined copper from Russia and Congo, another significant supplier, have shown minimal alterations despite the overall reduction in imports of refined copper.
Although China’s imports of refined copper have been decreasing, imports of copper raw materials, particularly from Russia, have been moving in the opposite direction. Import patterns for refined copper from Russia and Congo, another significant supplier, have shown minimal alterations despite the overall reduction in imports of refined copper.
This news about reduced copper demand has impacted copper prices in the market. Futures for copper at the London Metals Exchange and the Shanghai Futures Exchange have experienced declines, with traders exercising caution due to uncertainties about demand for metals in China. Shanghai’s metals projects anticipate that refined copper production will reach a record high in August, while aluminum prices have also seen a decrease in response to these trends.
Overall, the developments in China’s copper imports and manufacturing activity are closely watched by the global copper market, as they can significantly influence copper prices and supply dynamics.
Interested in learning more?
Sign up for Top Insights Today

Top Insights Today delivers the latest insights straight to your inbox.
You will get daily industry insights on
Oil & Gas, Rare Earths & Commodities, Mining & Metals, EVs & Battery Technology, ESG & Renewable Energy, AI & Semiconductors, Aerospace & Defense, Sanctions & Regulation, Business & Politics.



