U.S., G7 see China’s economic problems as systemic
- September 1, 2023
- Posted by: Quatro Strategies
- Categories: Business & Politics, China, United States

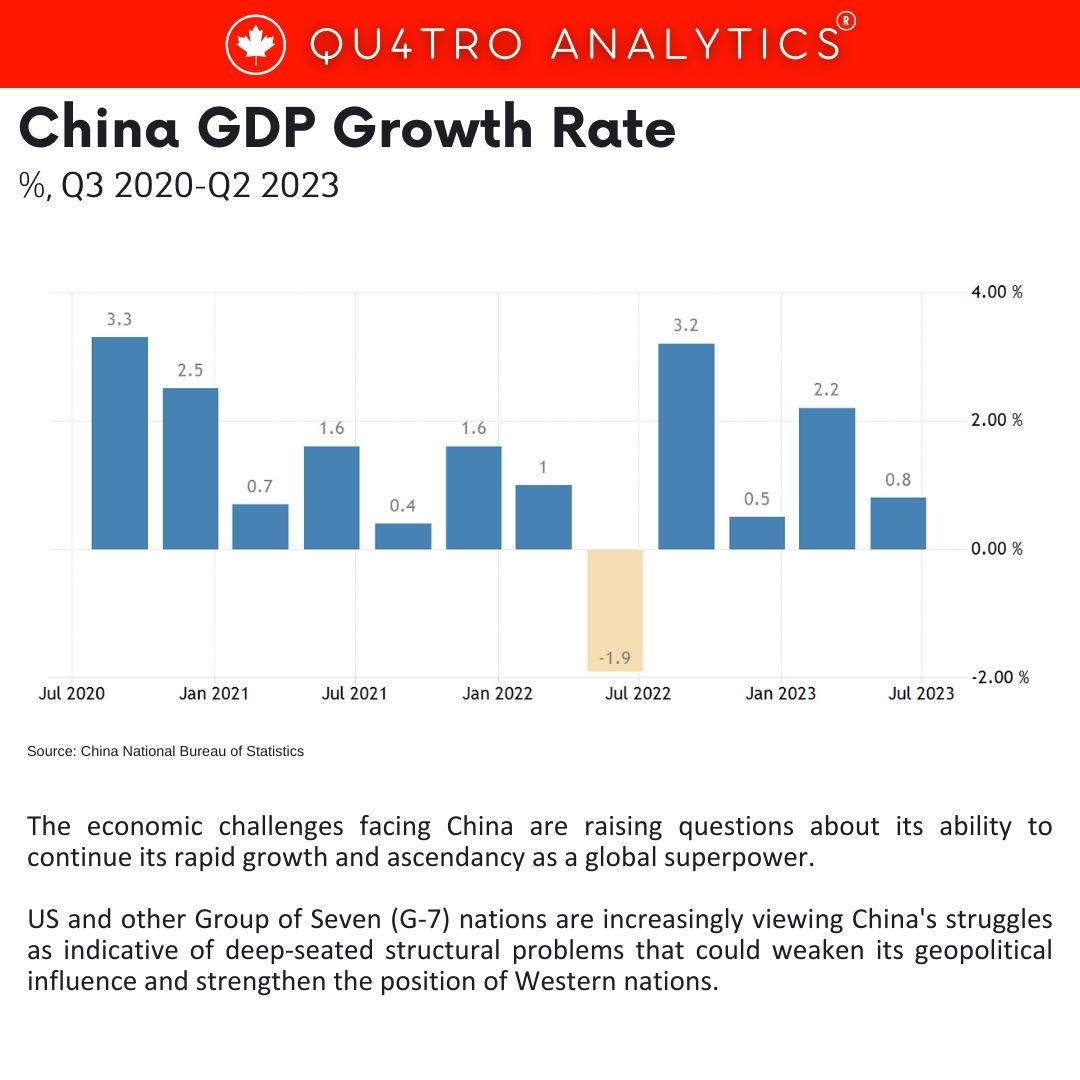
The economic challenges facing China are raising questions about its ability to continue its rapid growth and ascendancy as a global superpower. US and other Group of Seven (G-7) nations are increasingly viewing China’s struggles as indicative of deep-seated structural problems that could weaken its geopolitical influence and strengthen the position of Western nations.
While China once appeared to be on an unstoppable trajectory to surpass the United States as the world’s leading economic power, the prevailing sentiment in Washington and other capitals is shifting. The dominant economic narrative, which guided global capital flows for decades, is changing rapidly.
China’s economic slowdown, characterized by issues such as high debt levels, demographic challenges, soaring youth unemployment, and a collapsing real estate sector, has raised concerns about its long-term growth prospects. President Joe Biden referred to China’s economy as a “ticking time bomb,” and US Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo noted that American companies are increasingly finding China “uninvestible.”
The growing view is that China may be approaching a peak in its economic power, even if it is not yet in absolute decline. This perspective has been quietly gaining traction within the Biden administration.
 US officials believe that China has made a strategic mistake by resisting calls to open its economy further. While it is too early to definitively conclude that China is peaking or has peaked, long-term structural issues are seen as potential brakes on its growth. China’s policies, which create a less favorable environment for foreign investment and companies, are also contributing to these concerns.
US officials believe that China has made a strategic mistake by resisting calls to open its economy further. While it is too early to definitively conclude that China is peaking or has peaked, long-term structural issues are seen as potential brakes on its growth. China’s policies, which create a less favorable environment for foreign investment and companies, are also contributing to these concerns.
The economic challenges facing China are not limited to Washington. G-7 countries are contemplating the impact of China’s woes on their own markets, particularly as China has been a major driver of global economic growth. Some are concerned about the consequences of weaker Chinese demand and its effects on the global economy.
The shift in sentiment is also affecting Western policies, even though officials insist that they do not yet see a need to change course. The Biden administration’s recent limits on outbound investment in China were relatively weak and narrowly focused, partly due to lobbying by US investors. Additionally, the administration believed that China’s own hostile policies and economic strains were more effective in discouraging investment than US restrictions.
While officials argue that China’s slowdown validates their efforts to reduce dependence on the country and reassess trade, investment, and industrial policies, they acknowledge that China remains a formidable challenger in many strategic sectors. Therefore, Western nations are focused on strengthening alternative supply chains and bolstering their industrial policies.
In summary, China’s economic challenges are leading to a shift in the global economic landscape. While the narrative of China’s unstoppable rise is evolving, it is clear that China will remain a formidable economic rival for years to come. The implications of China’s economic struggles are far-reaching, impacting global markets, trade policies, and geopolitical dynamics. The key question now is whether China’s economic difficulties will lead to a more belligerent or more accommodative China on the world stage.
Interested in learning more?
Sign up for Top Insights Today

Top Insights Today delivers the latest insights straight to your inbox.
You will get daily industry insights on
Oil & Gas, Rare Earths & Commodities, Mining & Metals, EVs & Battery Technology, ESG & Renewable Energy, AI & Semiconductors, Aerospace & Defense, Sanctions & Regulation, Business & Politics.



